Introduction: The Dawn of 5G in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is at the forefront of the global 5G revolution, playing a critical role in shaping the future of connectivity. With leaders like China, South Korea, and Japan spearheading advancements, the region has witnessed a transformative expansion in 5G infrastructure. Over the last three years, substantial investments and policy reforms have accelerated this growth, positioning Asia-Pacific as a powerhouse in next-generation connectivity.
In this article, we would like to explore the rapid development of 5G in the region, examine the challenges that telecom operators face, and look forward to the promising future of the industry.
5G Adoption in Asia-Pacific: A Snapshot
Since the launch of the first commercial 5G networks in Asia-Pacific in 2019, adoption has soared. As of 2024, China, South Korea, and Japan account for more than 60% of global 5G connections, with China alone boasting over 1.2 billion 5G users. According to the GSMA, by 2025, Asia-Pacific is expected to have more than 1.4 billion 5G connections, making it the fastest-growing region for 5G globally.
Key Milestones:
- China: The undisputed leader in 5G, China has deployed over 2 million 5G base stations, covering nearly every urban center and major transportation hub. Leading telecom operators like China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom have aggressively invested in 5G infrastructure.
- South Korea: As one of the earliest adopters, South Korea’s 5G penetration reached 40% of its total population by 2024. With a highly dense network of 5G base stations, it offers one of the world’s fastest 5G services.
- Japan: While Japan’s rollout has been slower than China and South Korea, the country has ramped up its investments, driven by the demand for smart city solutions and autonomous technologies ahead of major global events like the 2025 Osaka Expo.
Recent Market Growth: Economic and Technological Impacts of 5G
The Asia-Pacific economy has seen dramatic gains from 5G, with the technology acting as a cornerstone of digital transformation across key sectors. A GSMA Intelligence report highlights that by 2025, 5G is projected to contribute $212 billion to the region’s economy, catalyzing innovation in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and entertainment.
Key Sectors Benefiting from 5G Expansion:
- Smart Cities: Asia-Pacific is home to some of the world’s most advanced smart cities, such as Shanghai, Seoul, and Tokyo. These cities are utilizing 5G to build robust IoT ecosystems that manage critical infrastructure, including traffic systems and energy grids. The technology enables real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making, improving urban efficiency and quality of life.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The rapid development of 5G has enabled progress in autonomous vehicle technology, with countries like Japan and South Korea leading the charge. 5G’s low latency and real-time communication capabilities allow vehicles to interact with their environment, paving the way for safer and more efficient transportation systems. V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication is a pivotal technology in this field.
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector has also benefited immensely from 5G, particularly in telemedicine. High-speed connectivity allows for real-time diagnostics, remote consultations, and the use of wearable devices for continuous health monitoring. These advancements are improving access to healthcare, especially in remote and underserved areas.
These developments are not only advancing the region’s technological landscape but also significantly boosting economic growth by enhancing productivity and fostering innovation. The expansion of 5G infrastructure, combined with future innovations in fields like IoT and AI, is expected to continue this trajectory well beyond 2025.
Projections for 5G adoption in the Asia-Pacific region
Graphic: 5G Adoption in Asia-Pacific (2021-2030)
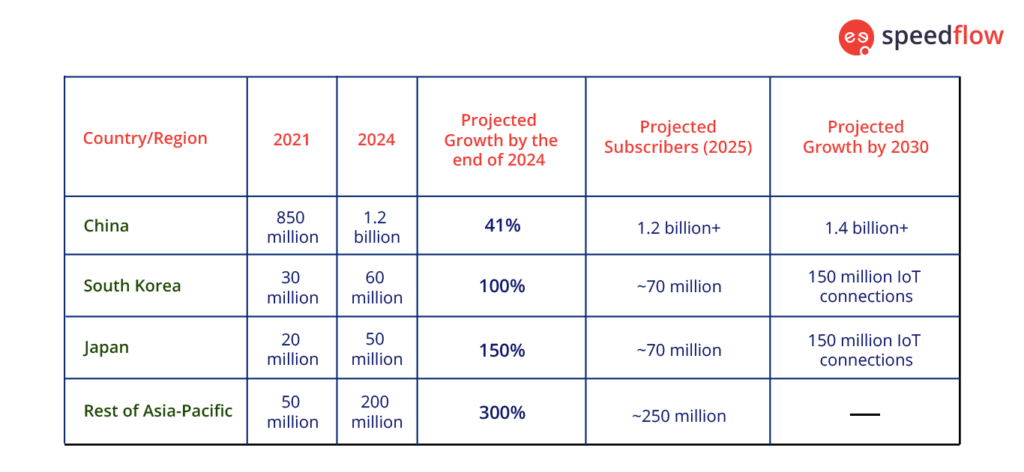
Projections for 5G adoption in the Asia-Pacific region suggest rapid growth, continuing through 2025 and into 2030. By 2025, the region is expected to reach around 1.2 billion 5G connections. A significant portion of this growth is driven by key markets such as China, South Korea, and Japan. The investment in 5G infrastructure across Asia-Pacific is substantial, with an estimated $227 billion expected to be invested by mobile operators between 2022 and 2025. By 2030, the number of 5G connections is projected to hit 1.4 billion, representing about 41% of all mobile connections in the region.
5G’s economic impact is also significant. It is estimated that by 2030, 5G technology could generate approximately $133 billion in economic benefits in the Asia-Pacific region. Countries like China and South Korea are already leading global 5G adoption, while emerging markets such as India are expected to witness rapid growth. Japan and South Korea are also driving advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT), with a projected 150 million IoT connections by 2025
- Projected Growth by 2030: While China, South Korea, and Japan have detailed forecasts, other parts of the Asia-Pacific region have more uncertainty due to diverse economic and infrastructural development stages. Some countries may only begin large-scale 5G rollouts after 2025, so projections are less precise.
- Economic Impact by 2030: Economic impact estimates focus more on major markets that are expected to lead 5G-related growth (e.g., China). For the rest of the region, specific economic impact data might be sparse due to less aggressive infrastructure spending and delayed consumer adoption.
Challenges and Solutions: Expanding 5G Coverage
While Asia-Pacific leads the world in 5G deployments, there are significant challenges that need to be addressed to maintain growth momentum. Rural and remote areas, especially in developing countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam, face connectivity gaps due to the high costs of infrastructure deployment.
Spectrum Allocation: A critical challenge in many countries is the delayed release of spectrum bands for 5G. Governments across the region are working to resolve these issues by holding auctions and revising policies to ensure that telecom operators can access the necessary spectrum at affordable rates.
Collaboration with Private Sector: Many countries are adopting public-private partnerships to finance 5G infrastructure. For example, India’s Digital India initiative involves significant collaboration between the government and telecom operators to enhance connectivity in underserved areas.
Future Projections: 5G’s Expanding Role in the Region
The outlook for 5G in Asia-Pacific is promising. By 2028, 5G technology is projected to contribute $360 billion to the region’s economy, fostering growth across multiple industries. As the region moves into the next phase of 5G expansion, the focus will shift toward 6G research, densification of networks, and the deployment of private 5G networks, particularly within sectors such as manufacturing and logistics. Enterprises in these fields will benefit from enhanced communication speeds, real-time data transmission, and lower latency, all of which are crucial for operational efficiency.
The deployment of private 5G networks is expected to accelerate, particularly for enterprises in sectors like manufacturing and logistics, where low-latency communication and real-time data exchange are essential. In addition to enterprise networks, smart cities and IoT ecosystems will benefit from further 5G densification, with more base stations and enhanced network capacity, ensuring seamless connectivity even in densely populated urban areas. As 5G continues to expand, telecom operators and governments are also exploring edge computing, AI integration, and advanced automation to harness the full potential of the technology, delivering new digital services to consumers and businesses alike.
6G Research or Preparing for the Next Generation of Connectivity
Even as 5G is still expanding, research into 6G technology is already well underway in the Asia-Pacific region. Leading countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have invested heavily in 6G development, with the expectation that it will provide even higher data rates, lower latency, and unprecedented network capacity. Early forecasts suggest that 6G could enable data transmission speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G, enabling innovations such as holographic communication, immersive virtual reality, and tactile internet applications. Research institutions and telecom operators are collaborating to explore terahertz frequencies, which could unlock new possibilities for ultra-high-speed data transfer. Governments are also creating 6G roadmaps, with China aiming to launch a 6G test satellite by 2025, positioning the region as a leader in next-generation connectivity. As research continues, standardization efforts and international cooperation will play a key role in defining the future landscape of 6G technologies.
Conclusion: Asia-Pacific’s Leadership in Global Connectivity
As we look toward the future, the Asia-Pacific region is positioned to remain a global leader in telecommunications innovation, driven by its commitment to 5G expansion and early leadership in 6G research. With 5G contributing $360 billion to the economy by 2028, the region will see widespread transformation across industries, particularly in smart manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and urban development. The continued densification of 5G networks and the adoption of private 5G by enterprises will provide the backbone for a more connected and efficient economy.
Meanwhile, the focus on 6G research and development will ensure that Asia-Pacific stays at the forefront of telecom technology, with countries like China, Japan, and South Korea leading the charge.




