In recent years, Africa has witnessed a remarkable surge in connectivity, with consortium models and changing mindsets playing pivotal roles in this transformation. As the continent embraces the digital age, the telecommunications industry is at the forefront of driving connectivity and fostering community engagement. This article goes deeper into the key aspects shaping Africa’s telecom landscape and explores the potential implications for hyperscale presence, regulatory dynamics, collaborative infrastructure projects, and evolving service procurement strategies.
Hyperscale Presence: Trust in the Continent’s Potential
One of the central questions in Africa’s telecom evolution is whether the trust in the continent’s potential will translate into increased hyperscale presence. With growing demand for digital services and the emergence of tech-savvy demographics, major players in the telecom sector are eyeing Africa as a key market for expansion. Consortium models, which involve collaboration among multiple stakeholders to pool resources and expertise, are facilitating the development of robust infrastructure to support hyperscale operations. By leveraging local knowledge and partnerships, telecom companies can navigate the unique challenges of the African market while tapping into its vast growth opportunities.
The hyperscale presence is not just a theoretical potential; it is actively taking shape. Tech giants like Google and Facebook have already invested in extensive infrastructure projects such as undersea cables and data centers. These investments are crucial for improving internet speeds and reducing latency, thereby making digital services more accessible to African users. Furthermore, local companies and governments are increasingly participating in these projects, ensuring that the benefits of such developments are widely distributed.
Current Africa Market Size and Growth
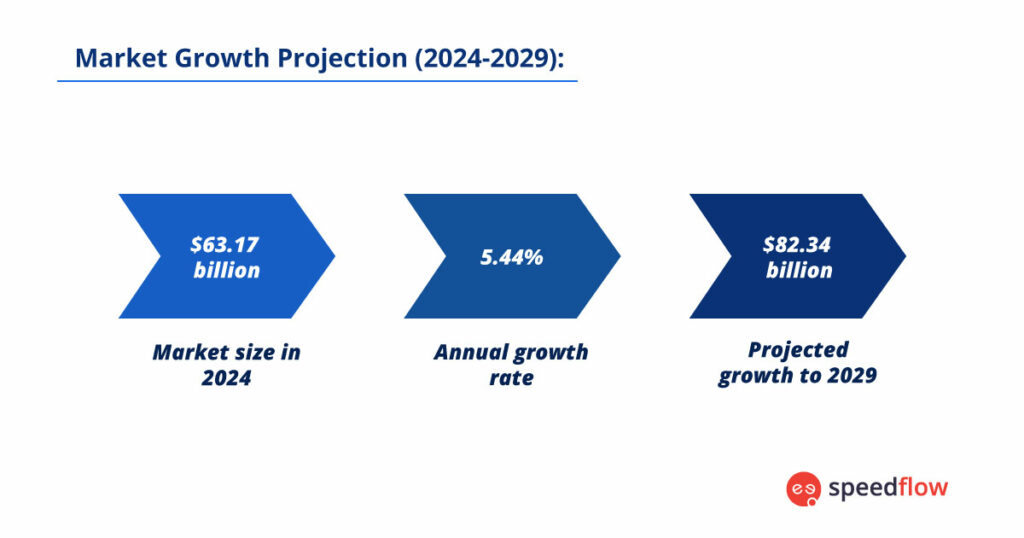
Africa’s telecommunication industry is changing rapidly, with the market worth about $63.17 billion in 2024 and projected to reach more than $82.34 billion by 2029, growing at a rate of 5.44% annually. This growth is closely linked to Africa’s young population. For instance, in Nigeria, with 60% of the population under 25 years old, there is a tech-savvy customer base hungry for online connections. Nigeria’s dynamic telecom sector, valued at $9.09 billion in 2024, is significantly influenced by MTN Group’s strategic partnerships and investments.
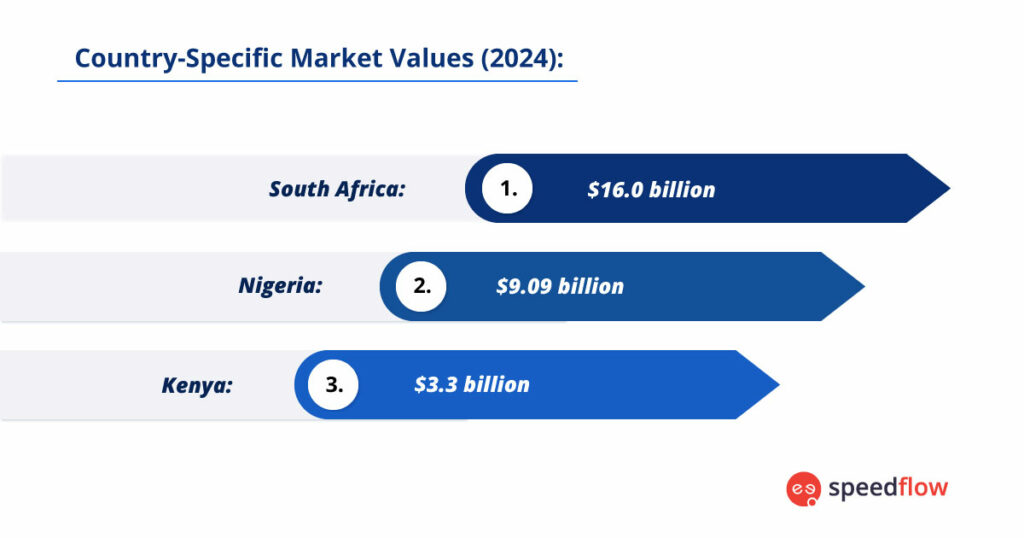
Kenya, an East African technological hub, had a telecom market worth about $3.3 billion in 2023. The total telecom service revenue in Kenya is projected to grow at more than 2% CAGR during 2023. Safaricom, a major player, has significantly contributed to the nation’s connectivity with innovations like the M-Pesa mobile payment service.
South Africa is a powerhouse in the African telecom market, with revenue from communication services expected to reach $16.0 billion by 2024. Vodacom is a key player, leading the country’s connectivity efforts through strategic alliances and partnerships, including collaborations with global telecom giants.
Economic growth, improved infrastructures, and strong digital advancements have transformed Africa’s telecommunication landscape. In countries such as Ghana and Ethiopia, a growing middle class is increasing the need for modern communication tools, leading to investments in developing telecom infrastructure. For instance, Kenya’s National Optic Fibre Backbone Infrastructure (NOFBI) project aims to enhance internet connectivity across the country and improve the delivery of e-government services.
Shifting Regulatory Environment: Navigating the Landscape
The regulatory environment in Africa is undergoing significant changes, posing both challenges and opportunities for Internet Service Providers (ISPs). As governments seek to promote competition and innovation while safeguarding consumer interests, ISPs must adapt to evolving regulatory frameworks. Compliance with data protection laws, spectrum allocation policies, and licensing requirements is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Additionally, partnerships with local authorities and industry stakeholders can help ISPs navigate the complex regulatory landscape and foster a conducive environment for sustainable growth.
A notable trend in the regulatory landscape is the increasing emphasis on data sovereignty. African nations are becoming more assertive about the need for data generated within their borders to be stored and processed locally. This shift requires telecom companies to invest in local data centers and cloud services, further boosting the infrastructure within the continent. Additionally, regulatory bodies are focusing on improving rural connectivity, ensuring that even the most remote areas benefit from the telecom evolution.
Collaborative Infrastructure Projects: Learning from the Subsea Playbook
Innovative approaches inspired by the subsea cable industry are reshaping terrestrial fiber projects in Africa. Just as submarine cables have revolutionized international connectivity, collaborative efforts are underway to enhance terrestrial infrastructure across the continent. By adopting consortium models and sharing resources, telecom operators and infrastructure providers can overcome logistical and financial barriers to infrastructure development. This collaborative approach not only accelerates the deployment of high-speed networks but also promotes digital inclusion and economic development in underserved regions.
The success of projects like the West Africa Cable System (WACS) and the Africa Coast to Europe (ACE) cable has demonstrated the power of consortium-led initiatives. These projects have significantly increased bandwidth and reduced internet costs, benefiting millions of users. Similar models are now being applied to terrestrial networks, with initiatives such as the Smart Africa Alliance working to unify and expand digital infrastructure across the continent.
Evolving Service Procurement Strategies: Meeting Changing Needs
As Africa’s telecom landscape evolves, service procurement strategies are also undergoing a transformation to meet the changing needs of consumers and businesses. From traditional voice and data services to emerging technologies like cloud computing and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, telecom operators are diversifying their service portfolios to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Additionally, partnerships with local startups and innovators enable telecom companies to offer tailored solutions that address the unique challenges and opportunities in Africa’s diverse markets.
The growth of mobile money services exemplifies how telecom companies are adapting to meet local needs. Services like M-Pesa in Kenya have revolutionized financial inclusion, providing banking services to millions who previously had no access to traditional banks. Similarly, telecom operators are exploring healthtech and edtech solutions to leverage mobile connectivity for broader social impact.
Forecast for 4G, 5G, and Beyond
Africa’s telecom future looks bright with advancements in 4G, 5G, and even potential 6G technologies. The 2021 International Telecommunication Union (ITU) statistics indicated that:
– 82% of Africa’s population had access to mobile broadband coverage,
– with 49% for 4G
– and 33% for 3G.
By 2029, nearly half of all phone connections in Africa are expected to be on a 4G network, which will continue to play a significant role in the market.
5G service subscribers are projected to grow rapidly, at 60% annually by 2029, increasing from around 11 million in 2023 to 180 million by 2029. 5G services have already been launched in several key African markets, including South Africa, Kenya, Zambia, Angola, Nigeria, and Zimbabwe. This rapid adoption indicates a robust future for high-speed connectivity across the continent.
The Road Ahead: Embracing Digital Transformation
The evolution of Africa’s telecom industry is a testament to the continent’s potential for digital transformation. With continued investment, innovative consortium models, and adaptive regulatory frameworks, Africa is poised to bridge the digital divide and emerge as a significant player in the global digital economy. The telecom industry’s role in this transformation cannot be overstated, as it provides the critical infrastructure needed to support a wide range of digital services and applications.
By embracing these changes and fostering a collaborative ecosystem, Africa can ensure that its telecom evolution benefits all its citizens, driving economic growth, and improving quality of life across the continent.




