You already know that VoIP works by transmitting data over the Internet – it is a phone call made through digital networks. However, the online world hides certain risks and there is always a danger of your corporate data falling into the wrong hands.That’s why SMBs and big corporations must prioritize VoIP security and better understand how to keep their telecommunication safe. In this article we will talk about VoIP encryption and what organizations can do to keep their data safe.
Is VoIP secure?
Yes, VoIP can be made secure if the entire infrastructure is properly protected. This requires steps towards the right direction by both the organizations and individual users. For example, relying on strong passwords is a must, but implementing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure tunnel for VoIP traffic, thus making it much more difficult for hackers to intercept the data. Continuous user training, regular audits, and updates help spot potential threats as early as possible. Firewalls and Session Border Controllers (SBCs) control the type of traffic that can access your network and prevent denial of service (DOS) attacks. Larger organizations have their own VoIP usage guidelines, including password policies, access policies and overall best practices. As you can see a lot can be done to strengthen the security of a VoIP network, but today we will take a closer look at encryption or coding of data to safeguard it from unauthorized access.
What is VoIP Encryption?
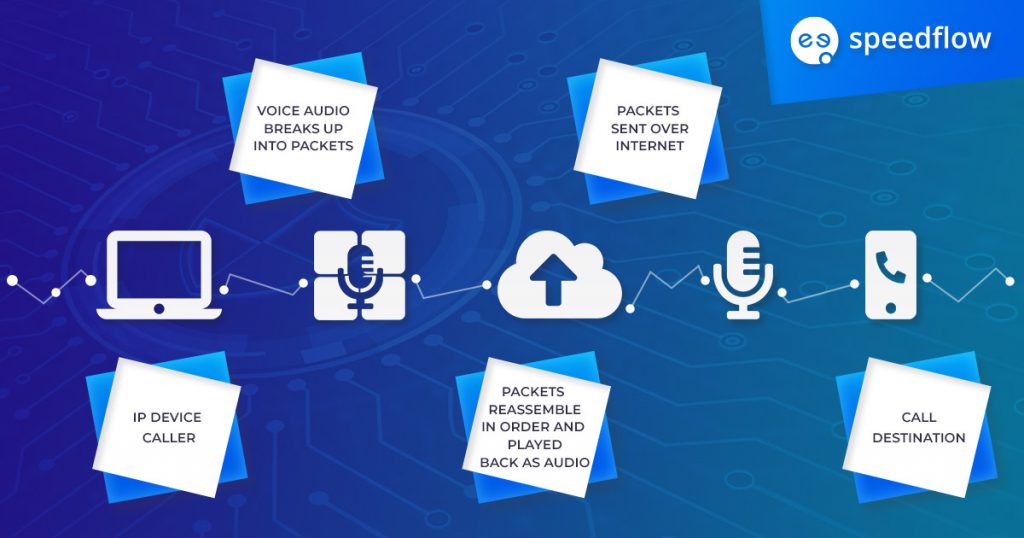
In VoIP communications, the voice data is digitized and then split into packets that can be sent over the internet. Encryption is the process of turning the data into a coded form to protect it from eavesdropping or interception during transmission over the Internet. Without encryption, these packets can potentially be intercepted and listened to, compromising the privacy and security of the call.
Below is a simple graph of how encryption actually works:
What is End-to-End Encryption?
If you have done some research on encryption lately or VoIP security in general, you have probably come across the term “End-to-End Encryption”. It is a security measure, which guarantees that only the sender and the intended recipient will be able to access the calls and messages. Third parties such as service providers, hackers, or even government authorities won’t be able to decipher the data. The key principle behind end-to-end encryption is that only the ‘ends’ of a conversation (i.e., the sender and the receiver) have the ‘keys’ to decode the conversation. No one else in the middle of the communication path, even the platform facilitating the communication has access to these keys.
Encryption Protocols in VoIP
There are several protocols that can be used to encrypt VoIP traffic, ensuring the data packets reach their final destination securely.
Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP): This protocol provides encryption, authentication, message integrity, and protection against replay attacks for RTP data, which is typically used for transmitting audio and video over IP networks.
Z Real-Time Transport Protocol (ZRTP): This is an extension of RTP, offering advanced features such as the Diffie-Hellman key agreement, which enables the keys for encryption and decryption to be generated and shared between the calling parties in a secure manner.
Transport Layer Security (TLS): This protocol provides security for communications over networks. When applied to VoIP, it’s often used to secure the signaling protocol SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), preventing the interception or tampering of call-setup information.
Secure SIP (SIPS): This is a version of SIP that uses TLS to provide a secure connection for call setup.
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec): This is a suite of protocols for securing Internet Protocol (IP) communications by encrypting each IP packet in a communication session. It can be used in combination with other protocols for additional security.
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS): This isn’t an encryption protocol itself, but it can enhance security when used with encryption protocols. MPLS is a type of data-carrying technique for high-performance networks that directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, and it can segregate VoIP traffic from other types of traffic.
Each of these protocols has its own advantages and potential drawbacks. The choice of protocol can depend on various factors, such as the nature of the data being communicated, the specific hardware and software being used, the need for interoperability with other systems, and the specific security requirements of the organization or individuals using the VoIP system.
Conclusion
We took a look at VoIP encryption, what it means, and why it is important for all organizations. Also, we addressed some general tips on boosting the security of communication infrastructures. Above all, every VoIP journey begins with choosing a reliable provider with a strong track record for security. Our MediaCore Class 4 Softswitch solution is equipped with a solid in-house security system, called The Guardian, which monitors your flow of traffic and keeps you notified about any suspicious activities.To learn more about it, please contact our team at info@speedflow.com.