What is a Softswitch in the Telecom industry?
The term is the acronym of Software Switch and it is used in VoIP core networks to control calls and process media streams. It can route VoIP calls & traffic across carriers and enable services such as switching elements, VoIP billing, directory services, network signaling, etc. It is safe to state that a Softswitch is the backbone of all VoIP communications.
In the past telecommunication networks relied exclusively on physical hardware switches known as circuit switches in order to establish connections between callers. Traditional telephone systems or landlines are an example of a technology that uses circuit switching. Due to the advent of software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV), Softswitches emerged as a more flexible and scalable alternative to their hardware counterparts.
Softswitches are responsible for several key functions in a network, including call media handling, signaling and call control. They enable the routing and switching of voice and data packets between different endpoints, such as telephones, computers, or other communication devices. Softswitches also handle tasks like call setup, termination, and feature management. Moreover, they can also provide advanced features such as call forwarding, call waiting, caller ID, voicemail, and interactive voice response (IVR) systems.They can be integrated with other network elements, such as gateways, media servers, billing systems, and application servers, to enhance the functionality and capabilities of the overall telecommunications infrastructure.
Softswitch Architecture
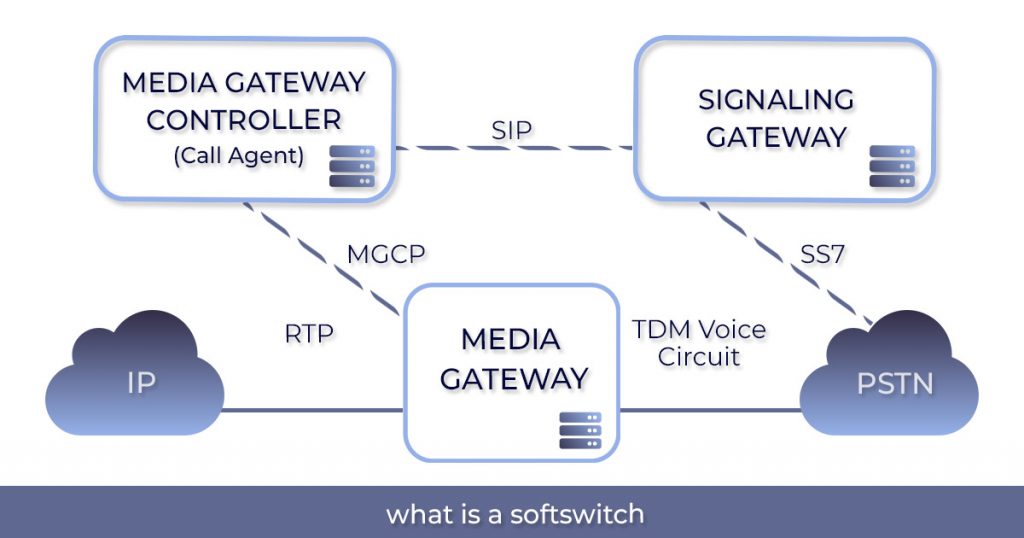
Now that we already clarified what is a Softswitch, let’s take a look at what its infrastructure looks like.
Call Control
It handles the signaling and call control aspects of the Softswitch, managing call setup, call routing and call teardown procedures. It uses protocols like Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) or H.323 to establish and control communication sessions between different endpoints, such as IP phones or other devices. The call control function also connects with other network elements, such as application servers or databases to perform additional services like call forwarding, call transfer, or voicemail.
Media Gateway
This component is responsible for handling the actual media streams during a communication session. It includes functions such as encoding, decoding, packetization and transmission of voice, video, or data streams. The media processing function can include features like echo cancellation, noise reduction, transcoding (converting between different media formats) and media quality monitoring.
It is also worth mentioning the role of session border controllers or SBCs in short. They are network components that protect VoIP infrastructures while enabling interworking between signaling messages and media flows (sessions). SBCs are used in carrier networks or enterprise infrastructures to provide fixed-line, mobile or commercial VoIP services. They are deployed at the border between private and public networks.
Types of Softswitch Classes
Softswitches are divided into 5 main categories, depending on the function they perform. Class 1 SoftSwitches are implemented in international gateways while Classes 2 and 3 are used to connect cities, towns, and states. Most carriers these days employ class 4 and class 5 softswitches, so let’s discuss them in a bit more detail.
What is Class 4 Softswitch?
When routing IP-IP calls to long-distance international locations using an IP network, class 4 is used. A call initiated from a class 5 in one location is transferred to the Class 4 Softswitch of the retail VoIP provider and then connected to the class 5 Softswitch at the other location. Class 4 Softswitch offers fewer features than class 5 Softswitch.
Concurrent calls
Protocol support & conversion
Intelligent calls routing
Secured firewall
Easy to use and simple interface
What is Class 5 Softswitch
All in all, a Class 5 Softswitch is routing large volumes of calls within a city, town, state, or country. Evidently, VoIP providers, cell phone carriers, and PSTN carriers are used to connect VoIP-enabled devices. When making a call from your device, the call is connected to your provider’s Softswitch, and then the call is routed to the correct IP address, SIP address, and DID number.
Auto-attendant
call forwarding
the call rules (find me/follow me/DND)
call transfer
the call waiting
caller ID
conference calling
E-911
enhanced voicemail
in-network calling music
ring/hunt groups
UCC
videoconferencing support
virtual numbers
Differences Between Class 4 and Class 5 Softswitch
As you may have understood so far, class 4 Softswitch is for routing calls over a long distance, while class 5 Softswitch focuses more on local call routing. However, the difference doesn’t end there.
Both Softswitches are different on the following key avenues:
Call Traffic Volume & Type
Functionality-wise, concurrent calls from multiple class 5 Softswitches are redirected to a single class 4 Softswitch. So, class 4 Softswitches are built to handle large volumes of calls at the same time. Class 5 Softswitch deals with smaller call traffic.
Intended Usage
As far as services are concerned, the Class 5 Switch serves as a handy retail solution. Besides, it also serves as an exchange in the PSTN, which is responsible for catering to the end-users and is located at the local telephone center. On the contrary, the Class 4 switch serves as a wholesale solution. It is a central office telephone exchange, which interconnects various local exchange carrier offices to establish communication over a long distance in PSTN.
Targeted users
Class 5 Softswitches are designed to work with both VoIP service providers and end-users. Class 4 Softswitches are made to serve wholesale VoIP solution providers, carriers, and Telco operators.
Routing Area
Class 4 can route a large number of long-distance VoIP calls across different networks and hence has a larger routing area. Class 5, on the other hand, routes SIP or IP address or a Direct Inward Dialing (DID) number of target users across a smaller area.
Benefits of using a Softswitch
By using Softswitches, organizations have observed the following benefits:
Scalable Solution:
Softswitches are generally easy to scale up or down, depending on the network’s size, compared to regular switches. A VoIP Softswitch can be scaled with the company’s growth and be upgraded with a simple download.
Accurate billing:
Providers may adjust call rates and produce exact invoices for each of their clients using VoIP Softswitches. As a result, Softswitches free up time and resources that organizations may put toward their main activities.
Highly Cost-effective:
VoIP carriers need to decide the ownership option that best suits their needs when it comes time to implement a Softswitch. There are three types of licenses: buyout, rental, and hosted. Analyzing which alternative is the most practical and economical is essential before beginning the implementation.
Versatile:
Routing, reporting, invoicing, and monitoring are all services that a VoIP Softswitch may accomplish. Softswitches may be integrated with other software to help businesses run more efficiently.
As you may have realized, there is no case of superiority when it comes to classes 4 and 5. Each is pivotal for providing seamless communication between different enterprises across the country.
However, depending on your specific line of VoIP business, the choice of a Softswitch solution that will meet your needs is not easy.
Overall, MediaCore SBC, as a Class 4 Softswitch, offers stable and secure VoIP call termination. Certainly, it is a cost-effective investment that ensures the seamless, intelligent, and efficient transmission of Voice and SMS messages. As a result, VoIP carriers will regain control of their call traffic.
We encourage telecom providers to test out MediaCore and select the best choice for their company. To learn more or to schedule a demo, get in touch with our software sales team at info@speedflow.com.